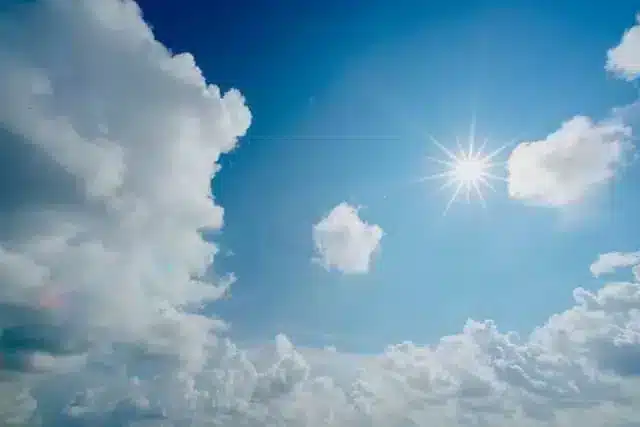

Solar irradiance measurements are a vital part of any planned solar installation. One of the first things any solar contractor will do before starting to design a system is to take a look at the level of solar irradiance the property receives daily and determine what the best panel placement and location will be for a system to perform at its best.
Whether you’re doing the solar irradiance calculation yourself or relying on software or third-party services to provide you with your shade reports, it’s crucial to understand how to get this data and how to use it to make the most out of it for every solar system you install. Read on to learn everything there is to know about measuring solar irradiance.
What is Solar Irradiance, and Why is it Important?
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area received from the sun at a given time. This is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). To calculate solar irradiance in the context of solar installations, solar irradiance is calculated for a yearly period to account for the rotation of the Earth, sun exposure on any given day of the year, and the seasons.
The resulting values of this integrated solar irradiance calculation are called solar irradiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation, and are displayed in kWh/(m2 day), or kWh/(m2 year).
This calculation provides solar professionals with the full picture of the amount of solar radiation hitting their client’s property throughout the year, enabling them to choose the best possible location for the solar installation so that the client gets the most out of their system.
Tools for Calculating Solar Irradiance
Solar contractors and designers have a few tools at their disposal to help determine the amount of solar radiation hitting a surface or location at any given time. Using these tools, contractors will need to head to the site of the potential solar installation to take the measurements themselves.
Actinometers
Actinometers are devices used to measure the amount of solar radiation hitting a given area at a given time. There are three types of actinometers available for various applications such as calculating solar irradiance values for solar installers, gathering data for meteorological purposes, or hydrology.
1 – Pyrheliometers
A pyrheliometer is used to measure direct radiation from the sun. It has a series of windowpanes that allow the sun’s rays to enter where they hit a thermopile, which can take this thermal energy and turn it into electric signals. These tools can assess how effective your solar panels will be in their given location.
The measurement from a pyrheliometer is called beam radiation since it also takes the circumference data.
Pyrheliometers are often used in solar tracking applications that enable ground-mounted systems to “follow” the sun for the highest efficiency level as the sun moves across the sky throughout the day.
2 – Pyranometers
Like pyrheliometers, pyranometers measure sun exposure. The difference between the two instruments is that while pyrheliometers measure direct solar radiation, pyranometers measure global solar radiation or diffused energy on a planar surface in W/m2.
To calculate the global solar radiation with a pyranometer, the formula for solar irradiance is expressed as follows:
Itot = Ibeam cosθ + Idiff
Pyranometer measurements will include the visible and non-visible parts of the spectrum and come in both digital and non-digital varieties capable of making the necessary calculations for you on the spot. For this reason, pyranometers are usually a great choice to determine the solar irradiance of a given location for solar panel installations.
Both pyranometers and pyrheliometers can be used independently based on the needed values. Still, they can also be used together for a fuller picture of the solar irradiance in a given area.
3 – Net Radiometers
Not really used for solar installation, net radiometers can measure incoming radiation
from the sun and sky and outgoing radiation from the ground. These are commonly found in the meteorology, climatology, and hydrology fields.
Photoelectric sunshine recorders
Also referred to as heliographs, photoelectric sunshine recorders measure the duration of the bright sun at a specific location. This is done with two photovoltaic cells made of selenium, one fully exposed and one covered.
When no beam radiation is present, the output of each cell is similar to the other, while when there is beam radiation, the recorder will display a difference. This allows the tool to determine bright sunshine hours available at a given location and help solar contractors with panel placement.
While older versions of sunshine recorders required a human to be present to record the data, newer models can do so electronically. They are also capable of measuring global and diffuse radiation levels. This makes them one of the best non-software tools a solar installer can use to calculate solar irradiance for PV panel design.
Other Devices
Solar installers might also be familiar with other PV-specific tools created specifically for solar power applications. These include the Solar Pathfinder, a device that displays a sun path diagram on a dome, and the SunEye, which will provide the user with a solar access percentage.
These devices often carry a high price tag and come with their own software to help users gather and analyze their results. In the past, these tools used to be the gold standard for collecting solar irradiance data but are slowly falling out of favor in light of new design software developments capable of handling many more aspects of the solar design process aside from simply calculating shading values.
Calculating Solar Irradiance with Software
With improvements to technology comes new ways for solar professionals to get the data they need to build efficient systems without any additional tools or trips to the site.
Combining complex algorithms with LIDAR data and using software tools to measure solar irradiance and generate shade reports is an incredibly quick and easy way to get the data you need to design the best possible system without all the extra work usually associated with using a tool such as a sunshine recorder.
What is a Shade Report?
Solar shade reports provide solar designers with a series of values aimed to guide their design process and enable them to determine which roof surfaces and locations receive the most sunlight daily to yearly. Shade reports can usually be viewed in your solar software or downloaded as a PDF.
Components of a Shade Report
Shade reports will include the following values for each facet of the roof:
- Solar Access Value (SAV): Measures the available clear sky over a location or the percentage of the energy that can be captured after taking into account the impact of shading
- Tilt and Orientation Factor (TOF): The percentage of the energy that can be captured based on the roof plane orientation and pitch. This does not account for shading.
- Total Solar Resource Fraction (TSRF): Calculated by multiplying the SAV by the TOF, this value measures the available solar energy in an area. This is the most helpful value for calculating solar production.
These values will be displayed in a series of tables containing each roof surface and the resulting percentages. The others will display the percentages on a month-by-month basis for each facet, giving visibility on the changes the roof will see in terms of solar irradiance as the seasons change.
No matter how you get your shade reports, they will all include the SAV, TOF, and TSRF values. A Solargraf shade report, which is created by using LIDAR data to generate a 3D model, on the other hand, is also capable of displaying additional roof measurements such as the dimensions and area, pitch, and azimuth of each roof surface. This extra information can also help a solar designer with the best and most efficient panel placement.
Why Choose Shade Reports Over Other Tools?
Using a Solargraf shade report will allow you to quickly and easily get the data you need to efficiently design your system and place panels intelligently without ever leaving the office. The additional data available in a shade report also helps to eliminate the need to visit the site since the roof measurements, azimuth, and line types are all available to the designer from anywhere.
Additionally, by plugging this data into Solargraf’s design tool, users will be able to view solar irradiance data on a pixel-per-pixel level, display a heatmap overlay over the home on the client’s solar proposal, and make it available for download to the client to give them the full picture as to why their system was designed the way it was.
Letting the client in on why you placed their panels in a certain way opens up the opportunity for them to ask questions and let the salesperson’s knowledge shine through. This puts the homeowner at ease while building trust that the salesperson is an expert and someone who has their best interests at heart, as they have worked out exactly how to get the most out of the roof in question.
Finally, dropping the shading devices and site visits will save solar professionals money. Less travelling back and forth to the site means less money spent on gas. Tools also cost money, with many ranging in the $100 – $200 range, while others will cost upwards of $2000. This money could easily be saved and reallocated to other parts of the business to better support company growth.
In Closing
Calculating solar irradiance and determining optimal panel placement for PV systems used to be a very math-heavy and time-consuming process. Nowadays, many solutions are available to help solar professionals get the information they need quickly and with less room for human error.
Solargraf’s solar design software can provide the shade data you need while also helping solar installers work smarter with team management capabilities, beautiful, customizable proposals with good, better, best options, speedy permits, financing integrations, and more. Book your free demo today to learn more about how Solargraf can help you grow your solar business and beat out the competition with less effort and more accuracy.



 United States
United States Germany/Austria
Germany/Austria Brazil
Brazil Netherlands
Netherlands Japan
Japan